Welcome to our article on Cameroon’s geographical location. If you’ve ever wondered “Where is Cameroon located?” then you’ve come to the right place. In this section, we will explore the fascinating positioning of Cameroon on the map and uncover its unique geographical features.
Key Takeaways:
- Cameroon is a country located in Central Africa.
- It is bordered by Nigeria to the west, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south.
- Cameroon’s latitude and longitude coordinates are approximately 6.5971° N and 12.3310° E, respectively.
- The country has ten administrative regions, each with its own unique characteristics and traditions.
- Yaoundé, the capital city, and Douala, the economic hub, are among the major cities in Cameroon.
Geographical Overview of Cameroon
Cameroon’s geography is as diverse as its rich cultural heritage. Located in Central Africa, Cameroon is often referred to as “Africa in miniature” due to its unique blend of landscapes and physical features.
One of the standout physical features of Cameroon is its impressive mountain ranges. The Mount Cameroon, an active volcano, is the highest peak in West Africa, standing at an awe-inspiring altitude of 4,070 meters. This majestic mountain not only adds to the country’s scenic beauty but also attracts adventurers and hikers from around the world.
As we explore further, we come across the Adamawa Plateau, a vast elevated region that stretches across the northern part of Cameroon. The plateau is defined by its rolling hills, grassy plains, and deep winding valleys, making it a prominent geographical feature.
Heading south, we encounter the dense rainforests of the Congo Basin, which cover a significant portion of Cameroon’s territory. These lush forests are home to diverse plant and animal species, including the endangered gorillas and chimpanzees.
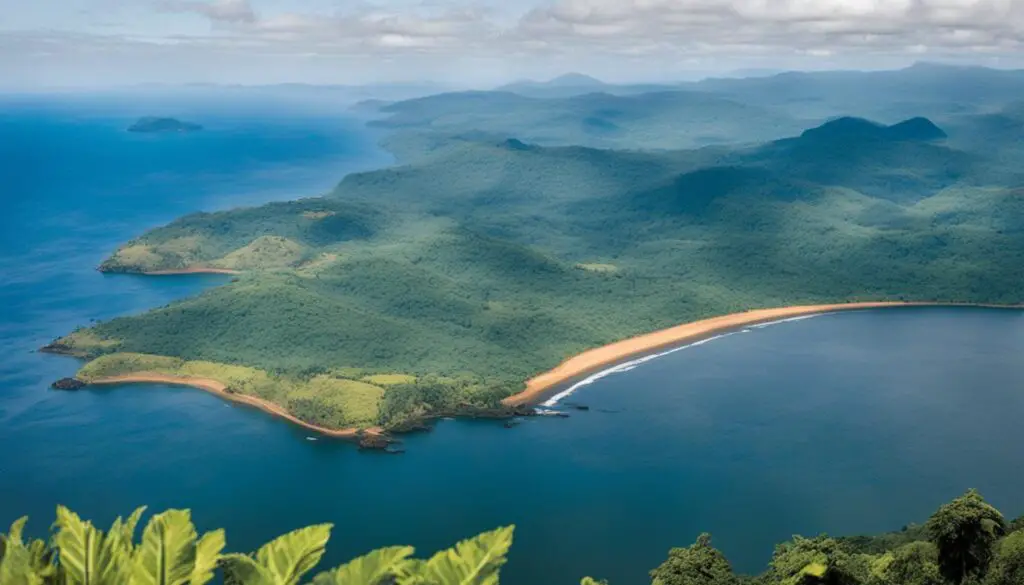

The coastline of Cameroon borders the Atlantic Ocean
Along its western border, Cameroon enjoys a beautiful coastline stretching approximately 402 kilometers along the Atlantic Ocean. This coastal region is characterized by stunning sandy beaches, picturesque fishing villages, and the vibrant economic hub of Douala – Cameroon’s largest city.
Cameroon’s geography also boasts an extensive network of lakes and rivers. The Lake Chad in the north, the Lake Nyos in the west, and the Sanaga River are just a few examples of the abundant freshwater sources that contribute to the country’s ecological richness.
In conclusion, Cameroon’s geographical diversity, encompassing mountains, plateaus, rainforests, coastlines, and waterways, offers a wealth of natural wonders waiting to be explored. This unique blend of physical features sets Cameroon apart and makes it a captivating destination for nature enthusiasts and adventurers alike.
Borders of Cameroon
Cameroon is surrounded by several countries, forming its borders with its neighboring nations. These countries play a significant role in shaping the regional context of Cameroon.
In the west, Cameroon shares its border with Nigeria, its largest neighbor and one of the most populous countries in Africa. To the east, Cameroon borders Chad, known for its diverse landscapes and cultural heritage. In the north, Cameroon’s boundary extends with Niger, a country rich in natural resources and historical sites.
Heading south, Cameroon shares its border with the Central African Republic, a landlocked country known for its rich biodiversity and unique wildlife. At its southernmost point, Cameroon forms a border with the Republic of Congo, renowned for its lush rainforests and ecological importance.
The diversity of these countries reflects the rich tapestry of cultures, traditions, and natural wonders present in Cameroon’s neighboring regions. This geographical proximity has not only shaped Cameroon’s history but also played a key role in facilitating trade, cultural exchanges, and regional collaborations.
To visualize the location of Cameroon and its neighboring countries, refer to the map below:
Location within Africa
Cameroon occupies a significant place in Africa, both geographically and strategically. Situated in Central Africa, Cameroon is bordered by several countries, including Nigeria, Chad, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, and Gabon. Its unique position allows for diverse cultural influences and trade opportunities.
With its coastal region along the Gulf of Guinea, Cameroon serves as a gateway to the Atlantic Ocean. This coastal stretch provides access to international waters and facilitates maritime trade, positioning Cameroon as a key player in regional commerce.
Furthermore, Cameroon’s location within Africa offers a blend of landscapes, ranging from lush rainforests in the south to the savannah in the north. Its diverse topography contributes to its ecological significance, housing a remarkable array of wildlife and natural resources.
Additionally, Cameroon’s strategic positioning in Africa makes it a hub for transportation networks. The country serves as a crossroad between West Africa and Central Africa, linking major trade routes and facilitating commerce between neighboring countries.
Moreover, Cameroon’s location within Africa grants it geopolitical importance. It fosters diplomatic relations and cooperation with other African nations, contributing to regional stability and the promotion of economic integration.
In conclusion, the position of Cameroon within the African continent is a defining factor in its cultural, economic, and political landscape. Its geographic location, diverse landscapes, and strategic placement make Cameroon a significant player in Africa’s growth and development.
Latitude and Longitude of Cameroon
Understanding the precise location of Cameroon on the global map requires knowledge of its latitude and longitude coordinates. Located in central Africa, Cameroon spans between approximately 2° to 13° North latitude and 8° to 17° East longitude. These coordinates determine its exact position on the Earth’s surface.
Cameroon’s latitude places it in close proximity to the equator, with the majority of the country lying within the low latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere. This positioning brings favorable tropical climate conditions and lush vegetation to the region.
Meanwhile, the country’s longitude indicates its eastward position from the Prime Meridian, which passes through Greenwich, London. Camaroon’s longitude places it in the eastern hemisphere, further defining its location within the continent of Africa.
The image above showcases the geographical visualization of Cameroon’s latitude and longitude coordinates, highlighting its significant placement in central Africa.
Regions and Provinces of Cameroon
Cameroon, located in Central Africa, is divided into ten administrative regions, each with its unique cultural, geographical, and historical significance. These regions, alongside their respective provinces, contribute to the internal organization and governance of the country.
From the fertile farmlands of the Adamawa Region to the stunning landscapes of the Northwest Region, Cameroon’s administrative divisions showcase the country’s diversity and richness.
North Region
The North Region, situated in the Sahelian zone, is known for its arid landscapes and unique flora and fauna. It comprises six provinces, including the capital city, Garoua, and is home to the Waza National Park, known for its diverse wildlife population.
West Region
The West Region, characterized by its highlands and verdant forests, consists of eight provinces. This region is known for its cultural heritage and is home to the vibrant city of Bafoussam, famous for its lively markets and traditional handicrafts.
Adamaoua Region
Situated in the central part of Cameroon, the Adamaoua Region is known for its agricultural productivity and picturesque landscapes. It comprises six provinces, including Ngaoundéré, the regional capital, and is a hub for livestock farming and crop cultivation.
South Region
The South Region is famous for its lush rainforests, diverse wildlife, and breathtaking waterfalls. With six provinces, including the vibrant city of Ebolowa, this region offers opportunities for eco-tourism and exploration of its natural wonders.
East Region
Home to the Dja Faunal Reserve, a UNESCO World Heritage site, the East Region boasts rich biodiversity and pristine forests. It consists of four provinces and is known for its opportunities in agriculture, mining, and tourism.
Littoral Region
Located along the Atlantic coastline, the Littoral Region is home to the economic capital, Douala. With four provinces, including the city of Limbe known for its stunning black sand beaches, this region serves as a major hub for trade and business.
Northwest Region
The Northwest Region, characterized by its mountainous terrain and picturesque scenery, is home to the town of Bamenda. With seven provinces, this region offers opportunities for adventure tourism, cultural exploration, and agricultural activities.
Southwest Region
The Southwest Region, known for its stunning coastline and rich cultural heritage, comprises six provinces. This region is home to the iconic Mount Cameroon, breathtaking beaches, and the historic city of Buea.
Center Region
The Center Region, encompassing the capital city, Yaoundé, is known for its political, administrative, and cultural significance. With ten provinces, this region serves as the heartbeat of Cameroon’s governance and houses important government institutions, museums, and cultural centers.
Far North Region
Situated in the Sahel region, the Far North Region is known for its Saharan landscapes and unique cultural traditions. With six provinces, including the city of Maroua, this region offers opportunities for camel trekking, cultural festivals, and exploration of its vibrant markets.
Each region and its provinces contribute to the rich tapestry of Cameroon, reflecting the country’s diversity, traditions, and natural beauty. Exploring these administrative divisions allows visitors and locals alike to discover the hidden gems and unique experiences that make Cameroon truly remarkable.
Major Cities in Cameroon
Cameroon is home to a diverse range of cities and towns that showcase the country’s cultural, economic, and historical significance. Let’s explore some of the largest cities in Cameroon and the unique experiences they offer.
Douala
Douala, located along the Wouri River, is not only the largest city in Cameroon but also the economic hub of the country. Its bustling port is a major gateway for trade and commerce, making Douala a vibrant and cosmopolitan city. Visitors can explore the lively markets, enjoy delicious local cuisine, and take in the stunning views of the Atlantic Ocean.
Yaoundé
As the capital city of Cameroon, Yaoundé is both a political and cultural center. It is known for its beautiful architecture, including the iconic Presidential Palace and the National Museum of Yaoundé. Visitors can immerse themselves in the rich cultural heritage of the city by visiting traditional markets, art galleries, and museums.
Bamenda
Bamenda, situated in the Northwest region of Cameroon, is known for its picturesque landscapes and vibrant local culture. This city offers opportunities for outdoor enthusiasts, with nearby attractions such as the scenic Bafut Mountains and Lake Awing. Visitors can also experience the customs and traditions of the local Bamileke people.
Maroua
Located in the far north of Cameroon, Maroua is a city that showcases the unique blend of African and Arabic cultures. It serves as a gateway to discovering the Sahel region, with its sandy landscapes and traditional Fulani villages. Visitors to Maroua can explore the vibrant markets, taste the local cuisine, and experience the warmth of the local hospitality.
Limbe
Limbe, nestled on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean, is a charming city known for its stunning beaches and lush botanical gardens. It is also home to the Limbe Wildlife Centre, which is dedicated to the conservation of endangered wildlife species. Visitors can relax on the beautiful black sand beaches, explore the vibrant marine life, and enjoy the breathtaking views of Mount Cameroon.
Garoua
Garoua, located in the North region of Cameroon, is a city that offers a glimpse into the country’s rich history and cultural heritage. It is known for its ancient mosques, traditional crafts, and vibrant festivals. Visitors can immerse themselves in the local culture by exploring the bustling markets and witnessing traditional dances and ceremonies.
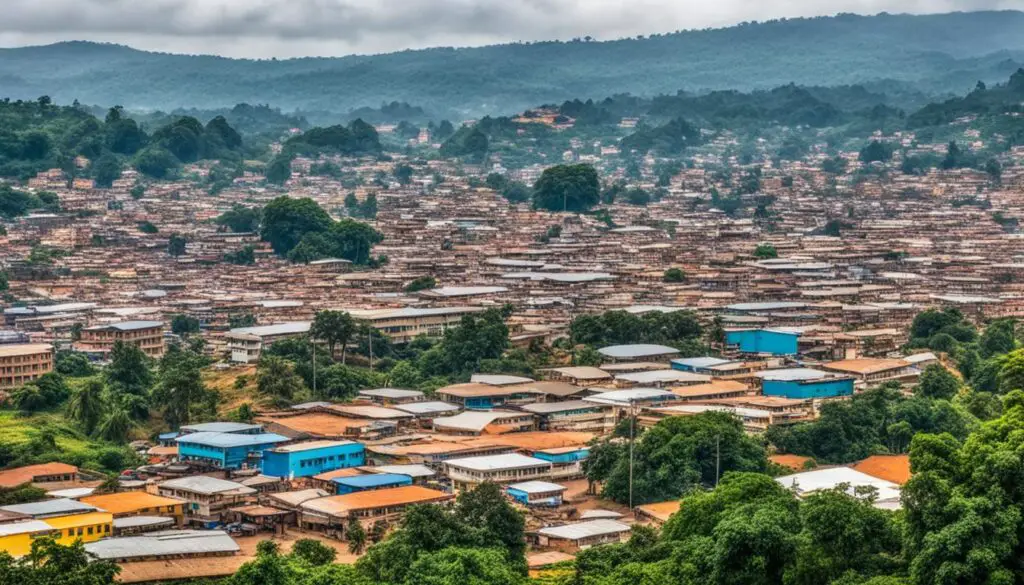

Natural Landscapes of Cameroon
Cameroon is blessed with an abundance of natural beauty and diverse landscapes that will leave you in awe. From lush rainforests to breathtaking mountains and picturesque coastlines, this African country has it all.
One of the highlights of Cameroon’s natural beauty is its rich biodiversity. The country is home to a vast array of plant and animal species, making it a paradise for nature lovers and wildlife enthusiasts. The dense rainforests, such as the Dja Faunal Reserve and the Campo Ma’an National Park, are teeming with life, with the chance to spot rare species like gorillas, chimpanzees, and elephants.
For those seeking adventure and scenic vistas, the diverse landscapes of Cameroon offer a range of options. The majestic Mount Cameroon stands tall as the highest peak in West Africa, providing a challenging climb and rewarding views from its summit. The stunning beaches along the Gulf of Guinea offer tranquil retreats, where you can soak up the sun and relax amidst the pristine natural surroundings.
But it’s not just the rainforests, mountains, and coastlines that captivate visitors. Cameroon is also home to breathtaking waterfalls, such as the Lobe Falls and the Ekom Nkam Falls. The cascading waters create a mesmerizing spectacle, inviting you to marvel at the sheer power and beauty of nature.
Exploring the natural landscapes of Cameroon is an opportunity to connect with the earth’s wonders and immerse yourself in the country’s natural heritage. Whether you’re trekking through the dense forests, admiring the panoramic views from mountain peaks, or simply relaxing on the sandy shores, Cameroon’s natural beauty will leave a lasting impression on your soul.
Importance of Cameroon’s Location
Cameroon’s strategic location plays a crucial role in its economic significance and regional stability. Situated in Central Africa, Cameroon enjoys a unique position that offers numerous advantages for trade and transportation.
The country’s placement at the crossroads of diverse regions contributes to its status as a key transit hub, connecting different parts of Africa. With its borders shared by Nigeria, Chad, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, and Gabon, Cameroon acts as a bridge between different cultures and economies.
Blessed with a vast coastline along the Gulf of Guinea, Cameroon benefits from access to international waters, opening up opportunities for maritime trade and commerce. The ports of Douala and Limbe serve as vital gateways, facilitating the import and export of goods.
Furthermore, Cameroon’s location grants it access to abundant natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and agricultural products. This wealth of resources contributes to the country’s economic growth and attracts foreign investment.
The strategic position of Cameroon also contributes to regional stability. Its central location allows for diplomatic engagement and cooperation with neighboring countries, fostering peace and security in the region.
In conclusion, Cameroon’s strategic location makes it an important player in the African continent and beyond. Its geographical advantages, such as its proximity to neighboring countries, access to international waters, and abundance of natural resources, contribute to its economic significance and regional influence.
Conclusion
Cameroon, located on the western coast of Central Africa, boasts a prominent geographical position that has significant implications both regionally and globally. As we have explored in this article, Cameroon’s location offers a variety of key takeaways.
Firstly, Cameroon shares its borders with six neighboring countries, including Nigeria, Chad, and the Central African Republic. This strategic positioning allows for cultural exchange, trade, and regional cooperation.
Secondly, within Africa, Cameroon holds a prominent place on the continent, geographically connecting West and Central Africa. Its diverse landscapes, from the coastal plains to the mountainous terrains of Mount Cameroon, contribute to its importance and appeal.
Lastly, Cameroon’s latitude and longitude coordinates precisely locate it on the global map, with an approximate location of 4.6128° N latitude and 13.1536° E longitude. Understanding these coordinates helps chart its position with respect to neighboring countries and the equator.
FAQ
Where is Cameroon located?
Cameroon is located in Central Africa, bordering Nigeria to the west, Chad and the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south.
What is the geography of Cameroon like?
Cameroon is known for its diverse geography, comprising coastal plains, savannas, mountains, and rainforests. It is also home to the highest peak in Central Africa, Mount Cameroon.
Which countries share borders with Cameroon?
Cameroon shares its borders with Nigeria, Chad, the Central African Republic, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo.
Where does Cameroon stand within Africa?
Cameroon is located in West-Central Africa and is positioned between the Gulf of Guinea to the southwest and the countries of Nigeria and Chad to the east.
What are the latitude and longitude coordinates of Cameroon?
Cameroon is situated approximately between 1.6500° N latitude and 12.6500° N latitude and 8.6500° E longitude and 16.2000° E longitude.
How is Cameroon divided administratively?
Cameroon is divided into ten regions, which are further divided into numerous provinces and subdivisions.
What are the major cities in Cameroon?
Some of the major cities in Cameroon include Yaoundé (the capital), Douala, Garoua, Bafoussam, and Bamenda.
What natural landscapes can be found in Cameroon?
Cameroon boasts diverse natural landscapes, including the savannas of the north, rainforests of the south, the volcanic terrain of Mount Cameroon, and the picturesque coastline along the Gulf of Guinea.
Why is Cameroon’s location important?
Cameroon’s strategic location offers significant economic advantages, as it serves as a transit point for trade between Central Africa and other regions. Its position also contributes to regional stability and cooperation.
What are the key takeaways about Cameroon’s location?
In summary, Cameroon is located in Central Africa and shares borders with multiple neighboring countries. Its diverse geography, major cities, and natural landscapes make it a significant player in the region. The country’s strategic location offers economic opportunities and contributes to regional stability.